MR. Robot Tech Terms for non-specialists ( no spoiler)
Written By  Idriss Douiri
Idriss Douiri
4 min read

MR. Robot is a great cybersecurity and hacking series that anyone can enjoy, even without any technical knowledge; however, understanding some nerdy terms will make it even better.
This article lists some key terms to know before or after watching MR. Robot, without spoiling the series.
Episode Naming Conventions
File Extension Naming (Seasons 1-3):
Episodes are titled to resemble pirated files found on torrent sites (e.g., eps1.0_hellofriend.mov, eps2.4_m4ster-s1ave.aes).
The titles frequently use Leet speak (e.g., swapping 4 for A, or 3 for E) and feature specific extensions that reflect the theme of each season:
| season | format | example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | video | .mkv, .mp4 |
| 2 | encryption | .tc, .p12 |
| 3 | archive | .so, .r00 |
These extensions are not random; they mirror the technical and psychological state of the protagonist in each chapter.
HTTP Status Codes (Season 4):
The final season switches to HTTP response status codes (e.g., 401 Unauthorized, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found).
These titles are thematic; the technical meaning of the error code often foreshadows the emotional state of the characters or the plot of that specific episode.
Devices / Hardware
- Rubber Ducky USB: A hacking tool that looks like a normal USB flash drive. When plugged into a computer, it disguises itself as a keyboard and types pre-programmed keystrokes at superhuman speeds (e.g., to open a terminal and download malware) in just a few seconds.
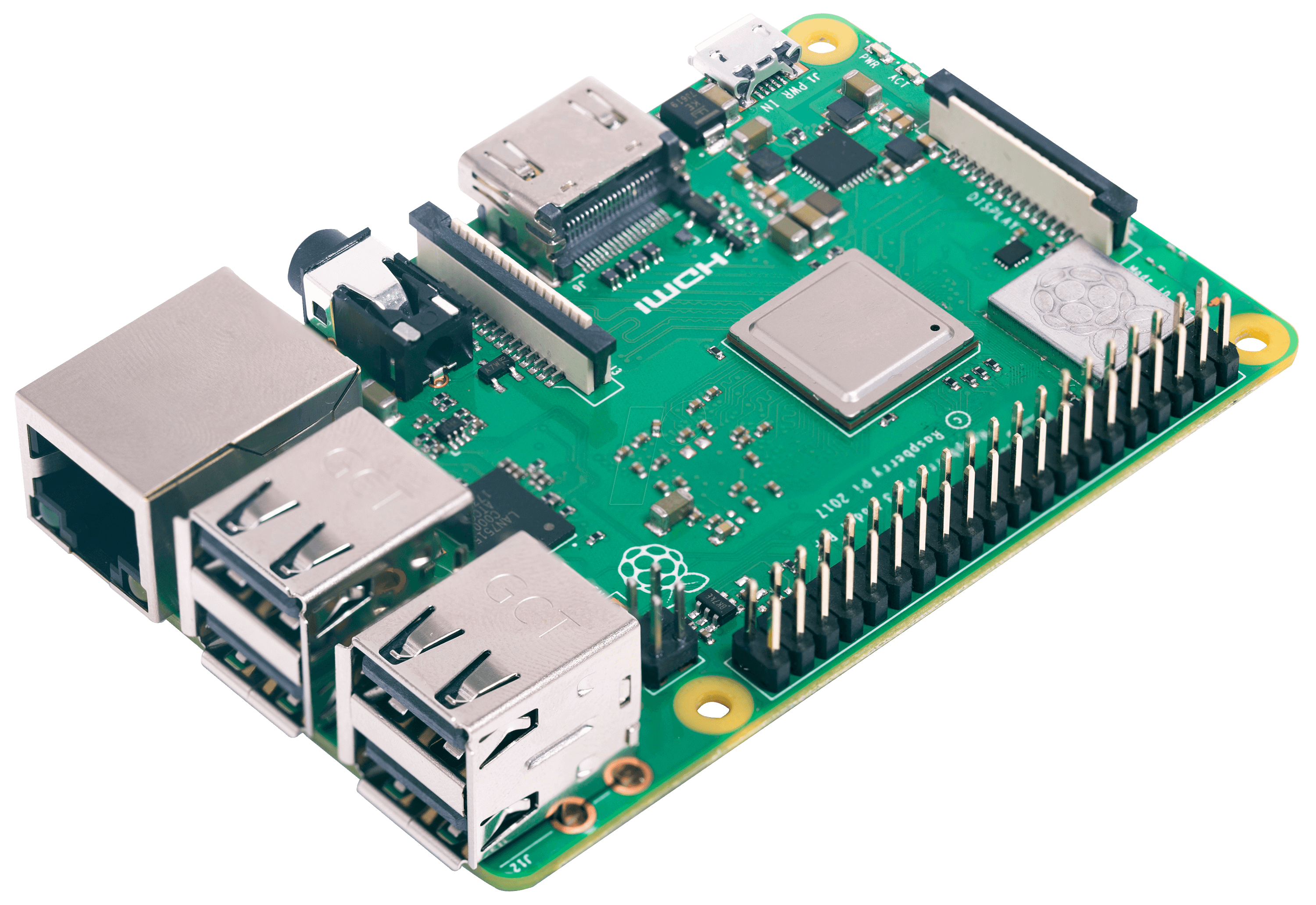
- Raspberry Pi: A credit-card-sized, inexpensive computer. Because of its tiny size and ability to run Linux, hackers often hide it inside physical locations (like under a desk) to act as a remote entry point into a secure network.
- Femtocell: A small, low-power cellular base station, typically used to boost signal in homes or offices. In a hacking context, it can be modified to act as a “fake cell tower,” tricking nearby phones into connecting to it so the attacker can intercept calls and text messages.
Software and Tools
- Kali Linux: The industry-standard operating system for penetration testing and ethical hacking. It is a Linux distro that comes pre-installed with hundreds of tools for network analysis, password cracking, and vulnerability assessment.
- Rootkits: A type of clandestine malware designed to give an attacker “root” (highest level/administrator) access to a computer while actively hiding its presence from antivirus software and the operating system itself.
- Tor (The Onion Router): A network that anonymizes web traffic by bouncing it through a series of volunteer relays around the world. It is used to browse the internet privately and to access “hidden services” (the Dark Web) ending in
.onion.
Tech Vocabulary
- Terminal: The command-line interface (usually a black screen with white or green text). Instead of using a mouse to click icons, the user types specific text commands to interact directly with the operating system, offering more power and control than a standard graphical interface.

- Binary: (or base-2 counting system) is the fundamental language of computers, consisting entirely of two digits: 0 and 1. All computer data, from text to images to programs, is ultimately stored and processed in this format. Binary can be one of two states (On or Off).
- Encryption: The process of encoding information using mathematical algorithms so that it becomes unreadable (scrambled) to anyone who does not possess the correct decryption key or password.
Attacks and Traps
- R.U.D.Y. (R U Dead Yet?): A “low-and-slow” Denial of Service (DoS) attack tool. Instead of flooding a server with massive traffic (like a DDoS), it opens a few connections and keeps them open as long as possible by sending data incredibly slowly, eventually exhausting the server’s ability to handle new users.
- Honeypot: A security mechanism acting as a decoy. It is a computer system set up to look like a vulnerable, valuable target (like a server with sensitive data). Its true purpose is to lure attackers in to monitor their behavior, waste their time, or catch them in the act without putting real data at risk.
- Ransomware: A type of malicious software (malware) that encrypts a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a payment (ransom) to provide the decryption key needed to unlock the data.